Welcome to Corius
We have one goal: to provide breakthrough technologies for transforming injured skin into healthy skin.
Corius is derived from the Latin word meaning skin. Corius is a division of Medline created to help empower the surgical community to advance quality healing and enable better outcomes for patients. At the heart of our commitment are clinicians, researchers, scientists and entrepreneurs driven to discover unique mechanisms of action designed to optimize the speed and quality of healing.
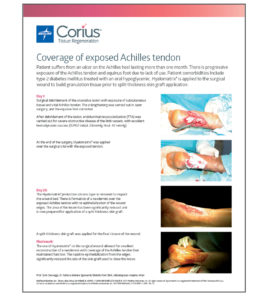
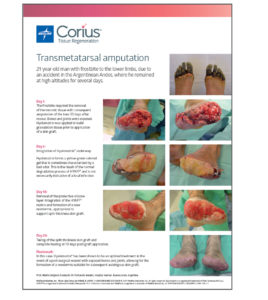
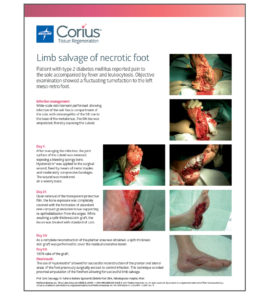
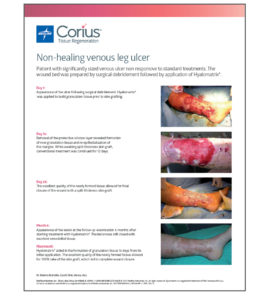
Hyalomatrix
Facilitate closure and help patients get back to their lives quickly.
Using the dermal regeneration properties of hyaluronic acid (HA), Hyalomatrix helps you rebuild tissue. HA is a main component of the extracellular matrix and is considered one of the key players in the tissue regeneration process.1 Hyalomatrix puts HA’s innate tissue regeneration properties in your skilled hands, helping you bring new hope to patients and their families. It features HYAFF, an exceptionally long-lasting form of HA. HYAFF delivers HA to the wound bed in a prolonged manner, facilitating each stage of the healing process.2-6

Clinical evidence
Hyalomatrix. Well-established. Well-documented.
The roles of HA, HYAFF and Hyalomatrix are supported by more than 800 peer-reviewed published papers.
750+
Exploratory research studies on hyaluronic acid
45
HYAFF technology studies
34
Hyalomatrix clinical studies
Published evidence
Request additional studies/pediatric studies from Medical Affairs.
References
- Litwiniuk M, Krejner A, Speyrer MS, Gauto AR, Grzela T. Hyaluronic Acid in Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration. Wounds. 2016 Mar;28(3):78-88. PMID: 26978861.
- Caravaggi C, Grigoletto F, Scuderi N. Wound Bed Preparation With a Dermal Substitute (Hyalomatrix® PA) Facilitates Re-epithelialization and Healing: Results of a Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Study on Complex Chronic Ulcers (The FAST Study). WOUNDS 2011;23(8):228–235. Available at: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/749515_1 Accessed June 18, 2018.
- Voigt J, Driver VR. Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives and Their Healing Effect on Burns, Epithelial Surgical Wounds, and Chronic Wounds: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Wound Repair Regen. 2012 May-Jun;20(3):317-31. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22564227 Accessed June 18, 2018.
- Gravante G, Sorge R, Merone A, et al. Hyalomatrix PA in Burn Care Practice: Results From a National Retrospective Survey, 2005–2006. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;64(1):69–79.
- Longinotti C. The Use of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Dressings to Treat Burns: A Review. Burn Trauma [Epub ahead of print] [cited 2014 Oct 16]. Available from: http://burnstrauma.com/temp/BurnTrauma24162-6158285_170622.pdf Accessed June 20, 2018.
- Moseley R, Walker M, Waddington RJ, Chen WYJ. Comparison of the Antioxidant Properties of Wound Dressing Materials–Carboxymethylcellulose, Hyaluronan Benzyl Ester and Hyaluronan, Towards Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species. Biomaterials (Impact Factor: 8.31). 05/2003; 24(9):1549-57.